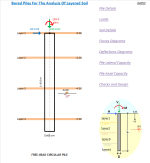
Bored Piles For The Analysis of Layered Soil.xlsx
Description
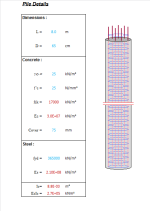
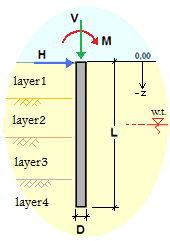
Pile Details
- Dimensions
- Concrete
- Steel
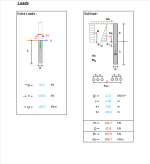
Loads
- Exta loads
- Soil loads
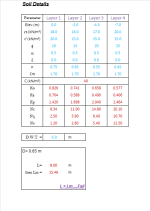
Soil Details
- Layer 1
- Layer 2
- Layer 3
- Layer 4
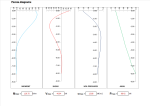
Forces Diagrams
- Moment
- Shear
- Soil pressure
- Axial
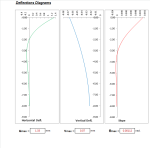
Deflections Diagrams
- Horizontal
- Vertical
- Slope
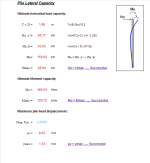
Pile Lateral Capacity
- Ultimate horizontal load capacity
- Ultimate Moment capacity
- Maximum pile head displacement
Pile Axial Capacity
- Bearing Capacity Factors
- Base Resistance
- Shaft Resistance
Checks and Design
- Shear Capacity
- Mechanical reinforcement ratio
- (m-n) interaction diagram
Solved using finite element methods
Related calculation for single layer.
Calculation Reference
Design of Concrete Piles
Reinforced Concrete Design
Civil Engineering Handbook
The analysis of bored piles for layered soil involves the following steps:
- Determine the soil properties of each layer, such as the soil type, unit weight, angle of internal friction, and cohesion.
- Determine the diameter and length of the pile.
- Determine the ultimate bearing capacity of the pile using one of the following methods: a. The static load test, which involves applying a static load to the pile and measuring the deflection and load. b. The dynamic load test, which involves measuring the acceleration of the pile and calculating the ultimate capacity using an empirical formula. c. Analytical methods based on the soil properties and the pile geometry, such as the Schmertmann method or the Broms method.
- Determine the skin friction and end bearing capacity of the pile for each soil layer based on the ultimate capacity and the soil properties.
- Calculate the total capacity of the pile by summing the skin friction and end bearing capacities of each soil layer.
- Calculate the allowable bearing capacity of the pile by applying a factor of safety to the total capacity, typically ranging from 2.0 to 3.0.
- Determine the required size and length of the pile based on the allowable bearing capacity and the design loads.
The analysis of bored piles for layered soil can be further refined by considering other factors, such as the presence of groundwater, the effect of soil stratification, and the effect of soil consolidation. The analysis can also be performed using computer software or spreadsheet programs, which can provide more accurate and efficient results.
Overall, the analysis of bored piles for layered soil provides a systematic and reliable approach to design and construct foundations that can support the required loads and ensure the stability and safety of the structures.
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.