Beam Flange Stresses

Description
Core Engineering Principle: Local Flange Bending Under Concentrated Loads
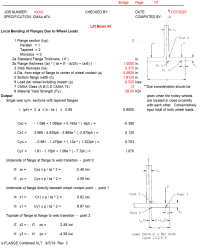
This calculation follows the principle that when a concentrated wheel load from a crane trolley acts on a girder flange, it creates localized bending stresses that are much higher than the general beam bending stresses.
1. Stress Concentration Effect
- When a wheel applies load to a flange, the load doesn't spread out evenly
- The flange acts like a small plate supported by the web, creating local bending
- This localized bending produces stress "hot spots" that can be much higher than the overall beam stress
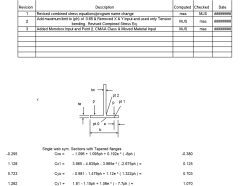
2. Critical Point Analysis The calculation examines stress at three critical locations:
- Point 0: At the flange-to-web junction (where support occurs)
- Point 1: Directly under the wheel contact point (maximum loading)
- Point 2: On the opposite side of the flange (tension/compression reversal)
3. Empirical Stress Coefficients
- The complex equations with coefficients (Cx0, Cx1, Cy0, Cy1) are empirically-derived formulas
- These come from extensive testing and finite element analysis by CMAA (Crane Manufacturers Association of America)
- They account for the complex 3D stress distribution around the wheel contact point
4. Load Distribution Consideration
- The parameter "ph" relates to how close the wheel is to the flange edge
- Wheels near the edge create higher stress concentrations
- The calculation includes impact factors since crane loads are dynamic
5. Combined Stress Analysis
- The local wheel stresses are combined with the overall beam bending stresses
- This ensures the total stress doesn't exceed material limits
- Different factors are applied for single web vs. box sections
This is essentially analyzing the same phenomenon that occurs when you step on a diving board - the local area under your foot experiences much higher stresses than the board as a whole, and these must be checked separately to prevent local failure.
Calculation Preview
Full download access to any calculation is available to users with a paid or awarded subscription (XLC Pro).
Subscriptions are free to contributors to the site, alternatively they can be purchased.
Click here for information on subscriptions.
Comments: 1
×
johndoyle-admin
7 months ago
Thanks for sharing your calculation! I have extended your XLC Pro subscription by 3 months by way of thanks.