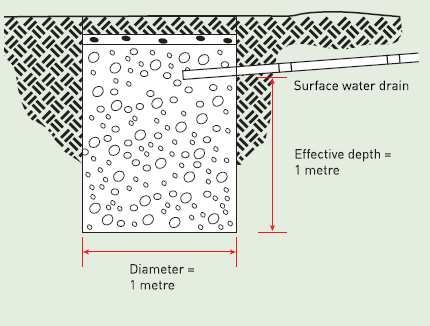
Fluids
4 ContainersFiles in Fluids
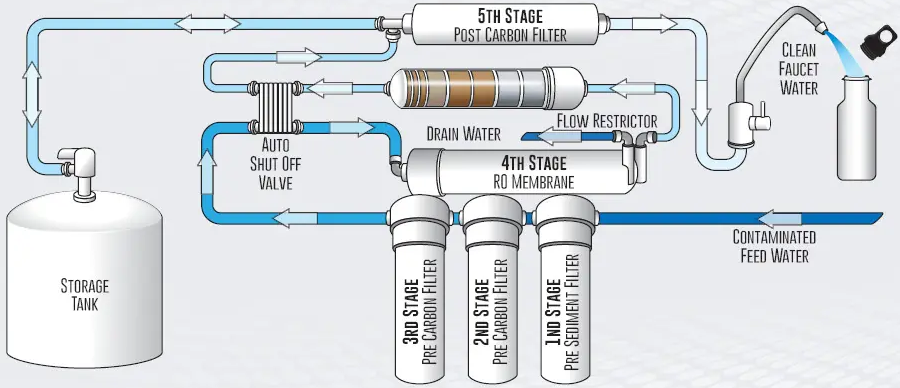
3-stage RO membrane system
Don't feel stupid if you've ever seen a news story about a terrible drought, then turned to your computer to see your pretty ocean beach screensave...
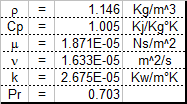
50-50 Ethylene glycol-water & air properties
This sheet will be of interest to those who work with coolant-coolant or coolant-air heat exhchangers. It will calculate certain prope...

CALCULATION OF CORROSION PROPERTY
THIS CALCULATION PROVIDES THE CORROSSION PROPERTIES OF FLUID BY CALCULATIN LSI & RSI.
Calculation Reference
Water Sca...

ChemicalProperties.xls
Calculate 468 elements or chemicals physical properties Notes:
- Only enter in the orange cells. Four drop-down, three nu...

Compressible Cake Constant Rate Filtration
Simulation of the batch sedimentation of compressible compacts is also possible using an appropriately coded computer spreadsheet. The...

Condensate Line Sizing
-
Amount of condensate flashed is calculated.
-
Further to above the density of the mixture (condensate+flashed steam) is found ou...

Cooling Tower Water loss Calculator
Cooling towers are used to dissipate heat from industrial processes or HVAC systems by transferring heat from the process fluid (usually wa...

Foam Calculation NFPA 11
NFPA committee activity in this field dates from 1921, when the Committee on Manufacturing Risks and Special Hazards prepared standards on ...
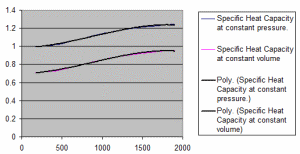
Properties of Dry Air.xls
The properties of dry air at various temperatures. Specific Heat Capacity at constant pressure. Specific Heat Capacity at constant vo...
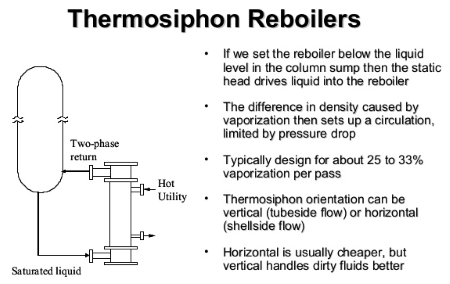
Thermosyphon Reboiler Hydraulics
Calculation Reference
Fluid mechanics
Thermosyphon Reboiler Hydraulics
Chemical Plant Desi...
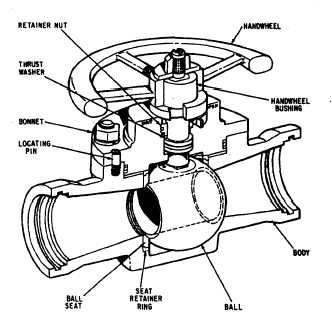
Valve sizing calculation for Gas and Liquid
SERVICE FLUID
FLOW RATE (1000 Kg/hr) MAX / NOR / MIN (w)
INLET PRESSURE (P1) BARA
OUTLET PRESSURE (P2) BARA
DELTA P -...